
When you hear the acronym "CIA", you might think of secret agents and spy movies. But in the world of cybersecurity and compliance, there is another CIA that is very important: the CIA Triad. This stands for Confidentiality, Availability, and Integrity, and it is a security model that helps you protect your organization from digital threats and security breaches.
This trio forms the backbone of a robust security model designed to fortify your organization's security infrastructure.
In this article, we will discuss each of these components and explain how you can apply them as part of your ISO-27001 compliance journey.
What is the CIA Triad?
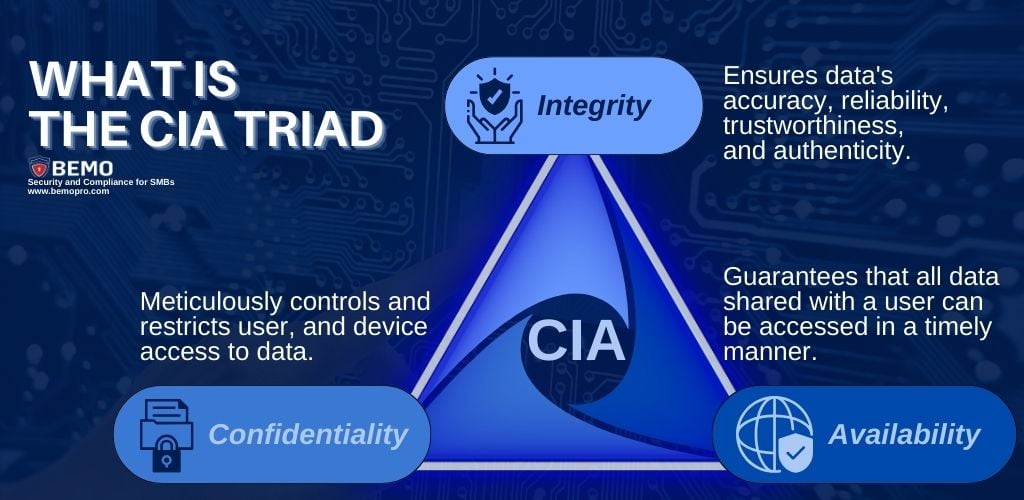
The CIA Triad is a fundamental concept in information security that outlines three core principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles serve as a framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating security policies, practices, services, and even products!
Confidentiality
In the CIA Triad confidentiality means ensuring that data is only accessible to specifically authorized individuals or systems. You must protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or alteration, whether done with malicious intent or by honest human error.
The primary goal of confidentiality is to fortify all data by meticulously controlling and restricting access. Only individuals with an absolute necessity for the information are granted access, ensuring a stringent approach to user permissions.
If there's no imperative need, data remains confidential, embodying a proactive stance in safeguarding information from unnecessary exposure or compromise.
Integrity
Integrity focuses on the accuracy and reliability of data. It ensures that information is not tampered with or altered by unauthorized entities.
Maintaining data integrity is vital for ensuring the trustworthiness of information, as any unauthorized changes could lead to misinformation or compromised system functionality.
Availability
Availability emphasizes the timely and reliable access to information and resources. It ensures that previously authorized users can access the required data or services when needed. Availability is essential to prevent disruptions in services and maintain the functionality of systems.
The CIA Triad is intricately woven into the fabric of the ISO 27001 standard. ISO 27001 is a globally recognized compliance framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Together, the CIA Triad and ISO 27001 create a comprehensive approach to information security, offering organizations a robust framework to safeguard their data against a diverse range of threats and vulnerabilities.
Read our article on “What is ISO 27001?” and learn more about this framework and its connection to the CIA Triad.
CIA Triad Examples and Use Cases
Now that you have a foundational understanding of the CIA Triad's principles—Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability—you may be eager to explore how these concepts manifest in day-to-day business operations and the specific policies and controls essential for upholding the triad's principles.
Let’s look at some CIA triad examples to show you the practicality of these pillars.
Confidentiality Controls and Use Case
Remember, these controls aim to restrict access to sensitive information. Think of tools that verify a user's identity and filter or limit who and where the information can be accessed from (device type and location). Some of these controls are the following:
- Data encryption
- Data classification and labeling
- Access Control
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
- Strong Password Policy and Management

- Let's consider the healthcare sector to exemplify the use of a component of Access Control, RBAC (Role Based Access Control), as a method to guarantee confidentiality.
A healthcare facility may have different administrative roles such as doctors, nurses, administrative staff, and billing specialists. With RBAC, each role can be assigned specific privileges. Doctors may have comprehensive access to patient medical histories, treatment plans, and test results to provide optimal care.
Nurses might have access to patient records for administering medications and updating treatment progress. Administrative staff may handle patient scheduling and general record keeping, while billing specialists could access information related to insurance and financial transactions.
This way all of them have access to the information they need to perform their job functions, without unnecessarily risking the patient’s data privacy and confidentiality.
Integrity Controls and Use Case
Integrity is all about keeping data updated and accurate. You should focus on having ways to visualize any changes and verify they are legitimate. If the information is inaccurate, that means there’s likely been a security breach. These are some of the controls for Integrity:

- Consider an e-commerce company that handles a significant number of daily online transactions, including customer purchases, order fulfillment, and payment processing.
By implementing robust logging and auditing systems, the e-commerce company can maintain a detailed record of each transaction.
This record includes essential information such as the timestamp, user details, and specifics of the purchase. If there is a modification in the order status or a change in payment details, the logging system captures these alterations.
In the case of any discrepancies or suspected security breaches, the company can refer to these logs to investigate and verify the legitimacy of changes. This not only enhances the organization's security, but also contributes to a positive user experience.
Imagine being a customer who places an important order, only to have it canceled due to a security breach. If a cybercriminal gained access to the system and manipulated account details, resulting in the loss or transfer of funds, it would be incredibly frustrating.
The detailed logs serve as a crucial tool for addressing such situations promptly and effectively, safeguarding both the company and the customer.
Availability Controls and Use Case
Availability controls focus on ensuring timely and reliable access to information and resources. Businesses implement redundancy strategies, backup systems, and disaster recovery plans to minimize downtime and guarantee continuous service. These are a few other availability controls:
- Firewalls and Proxy Servers
- Redundancy Strategies
- Backup Systems
- Disaster Recovery Plans
- High Availability (HA) Clusters
- Incident Response Plans

- Imagine a financial institution, such as a bank, that heavily relies on digital channels for customer transactions and services.
One of the servers hosting the online banking platform experiences a sudden software failure. In this case, redundancy strategies redirect user requests to backup servers, ensuring continuous availability of online banking services.
What’s Next?
Now that you’ve gained insights into the CIA Triad and know why it forms the bedrock of a resilient security model. Don't leave your organization vulnerable to threats—understand and implement confidentiality, integrity, and availability controls effectively.
If you’re ready to take the next step towards ISO 27001 compliance, book a meeting with our experts for personalized guidance on securing your information assets.
You can also further educate yourself on the topic by downloading our ISO-27001 brief and checking out some of our other articles about ISO-27001.
Top 10 Posts
-
Google Workspace to Office 365 Migration: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
Office 365 MFA Setup: Step-by-Step Instructions
-
How to Migrate from GoDaddy to Office 365
-
What is Microsoft Purview ? Your A to Z Guide to Getting Secure Fast
-
What is The CIA Triad?
-
How to remove Office 365 from GoDaddy (tips and tricks)
-
When Will CMMC 2.0 Be Required for DoD Contracts?
-
How to Set Up Office Message Encryption (OME)
-
Migrate From Gmail to Office 365: 2024 Guide
-
SharePoint vs. OneDrive (What's the Difference Again?)


Leave us a comment!