
Cloud computing has been around for a while now, but it’s only more recently that it has become a major focus of businesses worldwide. More and more, companies are expected to make the move to the cloud. The touted benefits range from increased productivity to improved efficiency, higher employee satisfaction, less operating expenses, and increased data security. Still, the knowledge that one should move to the cloud often precedes a clear understanding of what the cloud actually is. So, what exactly is the cloud? Read along to learn all about the cloud and why it will or won't work for you.
Table of Contents:
- What is the Cloud?
- Advantages of the Cloud
- Disadvantages of the Cloud
- How Can I Move My Business to the Cloud?
- Cloud Computing: The Way of the Future
First, it might be useful to know where the term "the cloud" came from. The origins are somewhat debated, but the most common belief is that at a tech conference in 2006, Google CEO Eric Schmidt was asked about Google’s new online services. In response, Eric stated “It starts with the premise that the data services and architecture should be on servers. We call it cloud computing – they should be in a ‘cloud’ somewhere. And that if you have the right kind of browser or the right kind of access, it doesn't matter whether you have a PC or a Mac or a mobile phone or a BlackBerry or what have you – or new devices still to be developed – you can get access to the cloud.” Thus, the term “the cloud” was hatched.

What is the Cloud?
Now that you know where the name came from, let’s get into exactly what the cloud itself is. In simple terms, the “cloud” is when you access files and programs over an internet connection instead of on your computer’s hard drive. In slightly more technical terms, it’s when you access any information stored in a datacenter via the internet.
Traditionally, you would store files on your computer’s hard drive, a USB drive, or an external hard drive (or if you want to go way back...remember floppy disks?!). When using the cloud, you have access to those same files on any device and from anywhere, so long as you have an internet connection. For instance, lets say you have a Word document that you created at your job in California. It needs to be edited and emailed out but you are visiting family in Vermont. Problem? Nope. Because that Word document is stored in the cloud, you can simply login to your Office (where Word lives) account from a family member’s computer, your personal laptop, etc., make the edits, and email it out. If there’s no computer around, you can even do all of this from your smartphone!
Essentially the cloud means that, instead of having to carry every file you'll ever need with you like some sort of file hoarding maniac, all of your files are at your fingertips (and ready to share) everywhere you go, at any time. Think of it like going from CDs (or tapes) to an iPod. Life changing, right? Welcome to the cloud.
Here's a short video to further get you up to speed with all things cloud:
OK, now that we know the basics, lets swim a little deeper in the cloud waters. You see, the cloud is much more than an easily accessible storage device. There are MANY aspects to cloud computing. The three most common forms are PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS which stand for Platform as a Service, SaaS (Software as a Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service. These three are so pervasive that you've probably used at least one of them without even realizing it. Here’s a more detailed explanation of the three services:
Software as a Service (SaaS): These are going to be your cloud application services, (think OneDrive, Dropbox, Outlook, Word, Excel, etc.). These are the most commonly used form of the cloud in business as well as personal (think Microsoft 365 Personal & Family). SaaS utilizes the internet to deliver applications, which are managed by a third-party vendor, to its users. Some of these services offer access to their products through a web browser, desktop application, or both. Examples of SaaS would be Microsoft Office 365 and Google’s Gsuite. Remember back in the day if you wanted software, you would have to make a trip to a Best Buy, Sam Goody, etc., buy the disc, bring it home, and install it? Well no more! Now all of that can be done with the click of a "Download Now" button.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS allows developers to focus on the improvement aspect of app development, as opposed to menial tasks such as managing software updates or security patches. PaaS gives developers a framework that they can build upon to create custom applications. Servers, storage, and networking can be managed by a cloud service provider while developers can maintain management of the applications. Examples of PaaS would be Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Cloud infrastructure services are made of highly scalable and automated computer resources. Think of a computer that allows you to use and pay for only what you need. Instead of paying for 100% of a computer’s resources when you only need 60%, IaaS allows you to just pay for that 60%. However if at some point you need to move up to 70%, you can easily do that as well. IaaS is also a fully self-service for managing and monitoring servers, storage, devices, etc. IaaS allows businesses to purchase resources on-demand and as-needed instead of having to buy hardware outright and risk paying for more than they need. Examples of IaaS are Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS.
Here is a really handy diagram to help you understand the differences between the various cloud solutions and who is responsible for each aspect. As you can see, the farther to the right you go, the less you are responsible for maintenance.
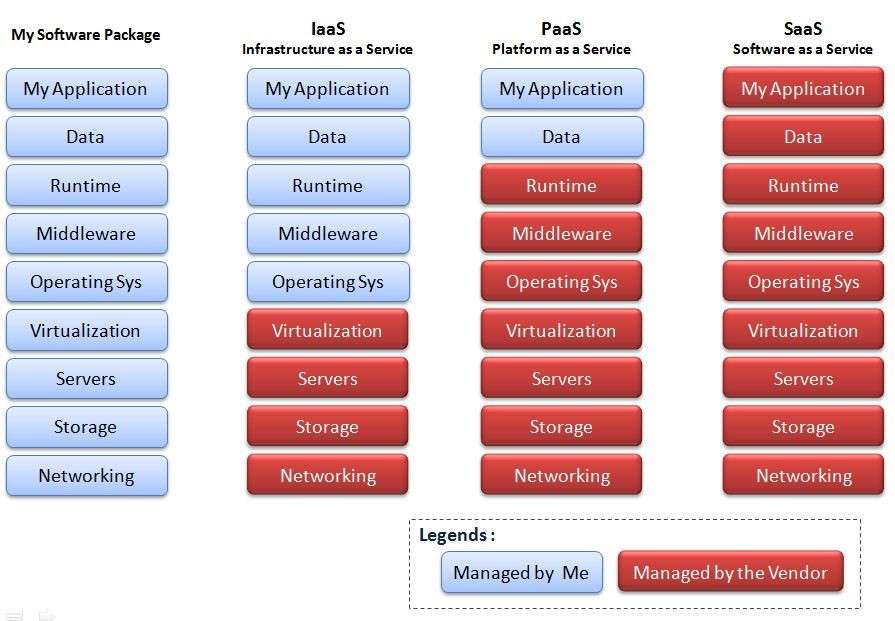
Advantages of the Cloud
Redundancy & Loss Prevention
When you upload a file to a cloud-based service such as OneDrive or Dropbox, it is sent to a datacenter. Datacenters are physical warehouses full of hard drives where all of your data is securely stored (read more about datacenters here). One huge benefit to storing data this way, is because of something called “redundancy”. Redundancy is where cloud service providers make copies of a file across multiple datacenters which ensures you always have that file available.

For example, let’s say you store a picture of your family's Thanksgiving last year in your OneDrive. Once you upload it, the picture is then securely sent to datacenter #1. Microsoft will then make copies of your picture and send it to datacenters #2 & 3. Now let’s say that there’s a bad lightning storm, and datacenter #1 is struck, which causes it to lose power. Instead of you having to wait for datacenter #1 to regain power, you will still be able to access your picture from datacenters #2 or #3 because of the redundancy. Basically, your photo display will never look like this:

All of this is done on the back-end, and you have no idea that the first datacenter was even down. Keep in mind, it’s extremely rare for datacenters to lose power, but it HAS happened in the past, which is why redundancy is extremely important.
Another benefit to cloud storage is loss prevention. Traditionally, you would store documents on your computer’s hard drive. However if your hard drive were to fail, unless you had backups of those files somewhere else, they would unfortunately be lost forever. We've all had that wheel of death moment or spilled on our computer or phone. Needless to say, it's not a good feeling.

Dry your eyes, little ghost because when you use cloud storage (OneDrive, DropBox, Google Drive, etc.) to store your documents they will always be securely stored in one of the various datacenters. So once you replaced the hard drive or computer or phone or simply logged on to another computer, you would easily be able to access everything again. Phew!
Ease of Accessibility
With the cloud, all your files and programs are available anywhere you have an internet connection. So, that family Thanksgiving picture you uploaded can be accessed by you or shared from any computer or mobile device. Really, your only limitation is your internet connection. As long as you’re not using a dial up connection or anything around that speed, you should have no issues. Not only can files be accessed from anywhere, but certain programs are also integrated into the cloud. For instance, Microsoft Office has an online version for all the apps in its suite, so that you can be productive even if you’re on your phone, tablet, or a computer other than your usual work device. Which brings me into the next benefit…
Flexibility of Work Practices
With the cloud, you can work from pretty much ANYWHERE as long as you have a good internet connection, and the country you are in doesn’t have blocks on any content you need to access. Here at BEMO, all of our employees are remote. We are spread out across the globe, yet we can collaborate and communicate as if we were in the same office. One of our employees pretty much moves to a new state or country every month, and he’s still able to work just as effectively as if he were in a cubicle next to me. Here's a snapshot of where our current employees work from:
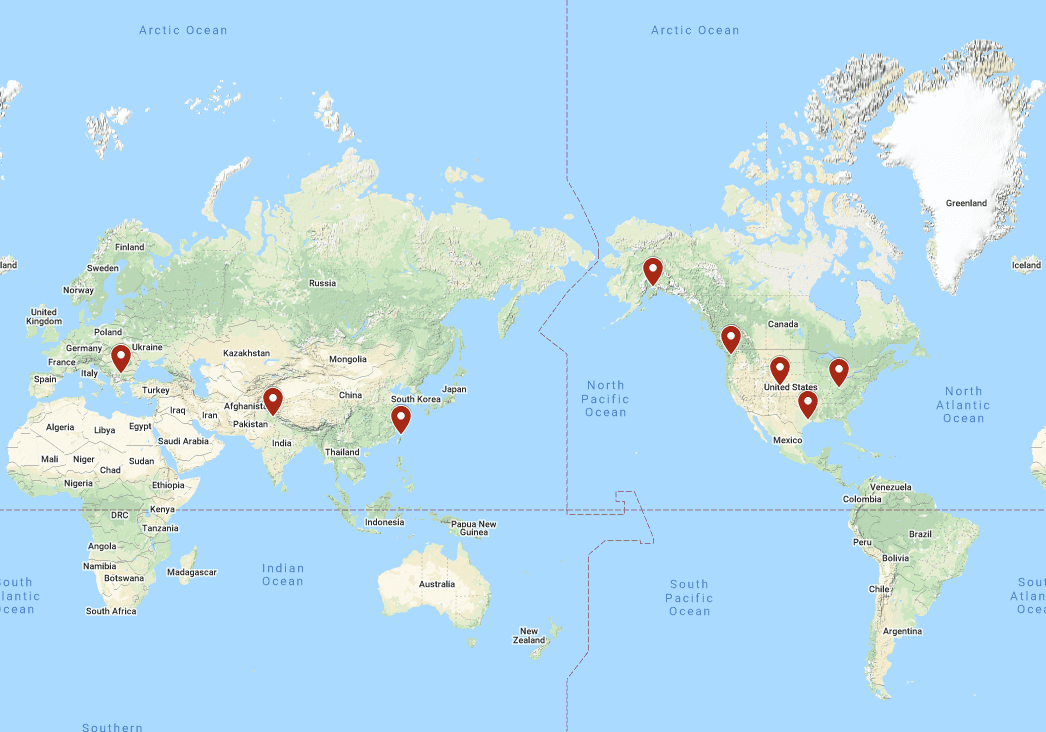
Having this flexibility also ensures that we always have a team member available if one of our customers needs assistance, because with people in pretty much every time zone, someone is always at work for you. Below is an awesome video showing how Microsoft has responded to the sudden demand in the ability for employees to work remotely.
Overall Cost
Traditionally, all of a company’s data was kept in and ran off of on-premise servers. Before cloud computing, a company would need several servers to run a business effectively. This was a very costly practice, because there were several things to factor in. Cost of the hardware and upkeep, cost of the electricity to run all of the servers, cost of the cooling systems to keep all of the servers running efficiently, and cost of IT personnel to maintain and update the servers.

With the cloud, a company can eliminate most if not all of these costs (aka: keep your money, don't give it away). When you move your business into the cloud, you’re pretty much just paying for the overall usage of the cloud resources, which can be scaled up or down depending on your need. The ability to scale resources is another way companies can save money. With on-premise solutions, even if you’re only using 50% of a server, you are still paying the costs to run 100% of it. You can't maintain half of it, power half of it or upgrade half of it. It's 100% or nothing. With the cloud, you can simply scale down your resources to whatever you need, and only pay for that usage. Therefore, a company can save a tremendous amount of money while still having all of their needs met and with room to grow.
Security
Cloud service providers always ensure they are using the latest forms of cyber security to protect their client’s data. Methods of providing cloud security include:
Firewalls: A network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Penetration testing (aka ethical hacking): The practice of testing a computer system, network or web application to find security vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
Obfuscation: Substitutes realistic but false data for the original to ensure privacy. It is used to allow for testing, training, application development, or support personnel to work with the data set without sharing sensitive data.
Tokenization: The process of turning a meaningful piece of data, such as an account number, into a random string of characters called a token that has no meaningful value if breached.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN): Provides a secure, encrypted tunnel to transmit data between a remote user via the Internet and the company network. Curious about VPNs and other remote tools? Check out our blog about the top tools for remote companies.
When maintaining your own on premise servers, it's up to you or your team to keep everything running top notch and top security.

Disadvantages of the Cloud
As with most things, there ARE a few disadvantages to using the cloud when compared to working from local machines. Yet as you will see, the pros far outweigh the cons.
Network Dependency
To make the most of the cloud, a business must always have an internet connection, there’s really no if’s, and’s, or buts about it. You need the internet in order access the files or programs that are hosted in the cloud.
If you lose your network connection because of a storm or an outage, you may experience some downtime. However, most large cloud service providers have a promise to deliver a Service Level Agreement (SLA) “A guarantee of a specific amount of uptime despite unforeseen issues” of around 99.9% uptime (meaning time when you can access your files) which is usually backed by a monetary value. Now that's a happy cloud!

Technical Issues
Due to the cloud being a service managed outside of your organization, if you ever experience any sort of technical issues, you have no choice but to call your cloud service provider for help. You cannot fix your cloud related problems in-house, and some smaller providers do not offer 24/7 support.
However, most if not all large cloud service providers, Microsoft and Amazon for instance, will offer around-the-clock customer support if any issues were to arise. Plus, the option of technical support means you don't have to be an expert, you can simply call one.

How Can I Move My Business to the Cloud?
There are several things to consider when moving to the cloud but all in all, your decision will be based depending on what your needs are. Do you want to move from an entirely on-premise setup (file server, SQL server, Citrix server, etc.) to a service such as Microsoft Azure to have it all in one place? Or are you simply wanting to store your company’s files in the cloud, while ensuring that your employees can work from anywhere?
Most commonly, the second option is what most small and medium businesses are asking for when they want to move to a cloud solution. Luckily, Microsoft has made it very easy for businesses to purchase and use cloud services with Microsoft 365. Below is a comparison of the most popular products for small-medium businesses that want to move their everyday business to the cloud.
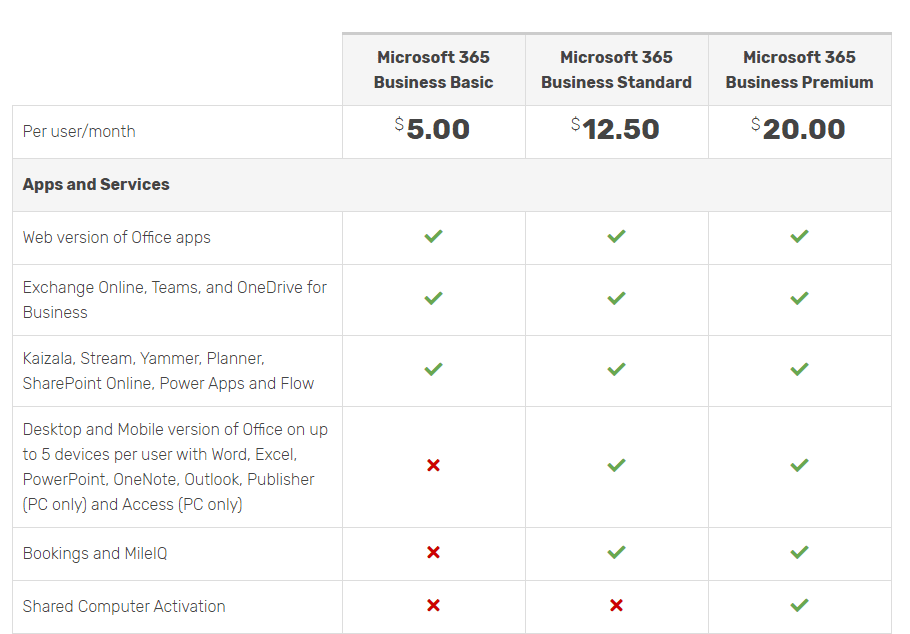
With Microsoft 365, your employees will have access to their files and documents in their OneDrive or your company’s SharePoint. They will also be able to collaborate remotely using Microsoft Teams.
Cloud Computing: The Way of the Future
You did it! You now have a general understanding of the benefits cloud services can offer in today’s connected world. Now, your decision as to whether the cloud is right for you fully depends on what you are looking to do with:
- Your particular business type
- How important remote access and secure file storage is to your company
- Whether or not you and your employees will have a reliable internet connection
Here at BEMO, we are constantly helping our customers make the shift (either full or partial) to the cloud. The main main motivators our customers cite for the switch? Overall costs (maintaining on premise equipment vs. going to the cloud) and allowing flexibility for their employees to work remote as opposed to being tied down to an office.

As you now know, cloud computing is becoming more and more prominent with businesses, regardless of size. I wouldn’t be surprised to see a huge majority of businesses make the switch within the next few years, and, as you also now know, there's good reason to do so. Every business is different. Now may be a very good time for you to weigh the pros and cons of moving to the cloud, and decide whether or not you’re ready to help your business become more future proof.
Curious if moving to the cloud is right for you? Use our Cloud Migration Cost Calculator at the link below:
Prefer to chat about your options? Schedule below to talk with our Team:
Top 10 Posts
-
Windows 10 Pro vs Enterprise
-
Migrate From Gmail to Office 365: Step-By-Step Guide
-
Windows 10 Enterprise E3 vs E5: What's the Difference?
-
What are the 4 types of Microsoft Active Directory?
-
How to Migrate from GoDaddy to Office 365
-
Google Workspace to Office 365 Migration: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
How to Set Up Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection
-
10 Benefits of Microsoft Teams
-
Top 3 Reasons to Move From Google Drive to Microsoft OneDrive
-
How to remove Office 365 from GoDaddy (tips and tricks)
-2.png?width=1080&height=1080&name=Untitled%20design%20(5)-2.png)





Leave us a comment!